A hemorrhoid, also known as piles, is associated with swollen blood vessels around or inside the anus and rectum. These hemorrhoidal veins are present in the lower part of the anus or rectum. On swelling up, these veins become thin, extended and irritated as the bowel passes through rectum or anus. Hemorrhoids may be external or internal depending upon the location. It has a high prevalence all over the world with around 50% people developing piles at some point of time in their life.
These occur more commonly in elderly as well as pregnant females.
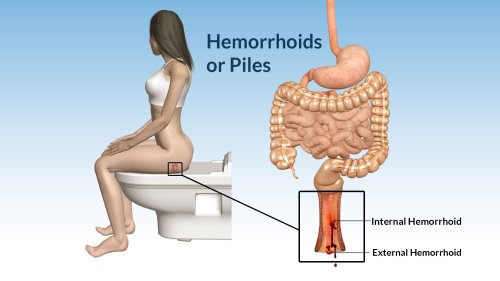
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Although the exact cause for hemorrhoids is still unknown but hemorrhoids may be caused due to varicose veins which may be inherited or weakness in the veins present in the rectum and anus. Extreme abdominal pressure may lead to swelling up of veins that become susceptible to irritation. Sitting or standing for long durations, obesity, straining on the toilet, pregnancy, sneezing, coughing, vomiting and holding the breath for long time are some of the factors that may exert pressure on these veins.
Piles is also related with diet. Eating more fibrous diet helps in preventing hemorrhoids while eating processed foods may increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids. Constipation causing factors like inadequate liquid intake or low fibre diet may also irritate the swollen veins, aggravating piles.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of piles include:
- Presence of bleeding from the anus. One may see bright red streaks of blood along with bowel or on toilet paper especially while passing out stools. Sometimes the bleeding can be chronic and profuse with more than just streaking.
- Pain or tenderness during bowel movement.
- Discharge of mucous fluids from anus
- Presence of a lump or swelling inside and/or around the anus
- Itching inside the anus.
- Excess hemorrhoidal bleeding however may also lead to anaemia in few cases.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be diagnosed by careful clinical examination by the doctor where the doctor examines the anus either with gloved and lubricated finger or through anoscope or a protoscope that are inserted inside the rectum. Other ways may be through colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy which include insertion of a flexible tune for viewing the deeper parts of rectum or colon. Barium enema followed by X-ray of lower gastro-intestinal tract may also be helpful.
It is necessary to rule out other diseases associated with anal bleeding. These include Crohn’s disease, anal fissure, colitis and colorectal cancer.
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
One should take necessary measures to prevent the aggravation or occurrence of hemorrhoids. Below are a few ways:
- Modification of diet and lifestyle- eating more of fibrous foods and less of processed food.
- Regular exercise and physical activities to prevent side effects of sedentary lifestyle
- Taking measures to prevent constipation by intake of adequate fluids and laxatives.
- Avoid prolonged sitting in toilet and avoiding straining while bowel movement.
Treatment for Hemorrhoids
Although hemorrhoids may settle down themselves without any treatment, the following measures can be adopted to treat it:
- Creams and ointments – Corticosteroid creams or suppositories maybe applied to the back area to relieve swelling and inflammation. These can be applied 5-7 times a day.
- Warm sitz baths for about 15 minutes 4-5 times in a day or the same number of times as of bowel movement
- Analgesics like paracetamol for alleviating pain and inflammation. These should be consumed in limited quantity as they may increase the sensitivity.
- Local anaesthetics for temporary relief of pain
- Laxatives to relieve constipation. Laxative could be either bulk forming or osmotic to increase the water content of stools and make them softer.
- Diet modifications during pregnancy. One must consult the dietician or gynaecologists for the diet modification.
If the symptoms don’t subside, other measures may be taken by the doctor and include:
- Sclerotherapy or injection with a scar forming solution to close the hemorrhoid. It is used as an alternative to banding.
- Rubber band litigation in case of prolapsed hemorrhoids. This is done to lower down or remove the blood supply to the hemorrhoids.
- Cauterization and coagulation using laser beam or electric probe or infrared light.
- Surgery for the removal of grade three or grade four internal hemorrhoids. Learn more about surgery.
